From Gaming to Healthcare: Expanding Horizons with VR and AR
Introduction
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have evolved from niche technologies primarily associated with gaming to become indispensable tools across a wide range of industries. Once confined to entertainment, these immersive technologies are now transforming sectors such as healthcare, education, training, and retail. This article explores the diverse applications of VR and AR, highlighting their impact on healthcare and other industries.
The rapid advancement of VR and AR has opened up new possibilities, enabling more realistic simulations, enhanced learning experiences, and improved patient care. These technologies are not just changing how we interact with digital content but also how we approach complex challenges in various fields.
Section 1: VR and AR in Healthcare
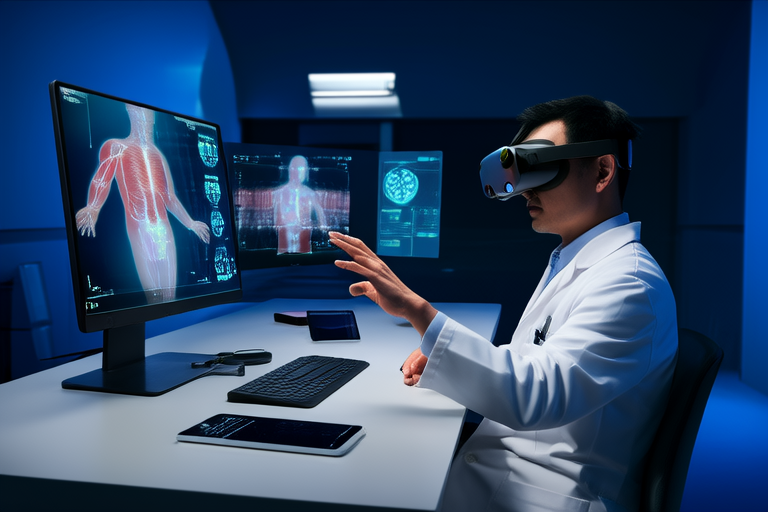
Medical Training and Simulation
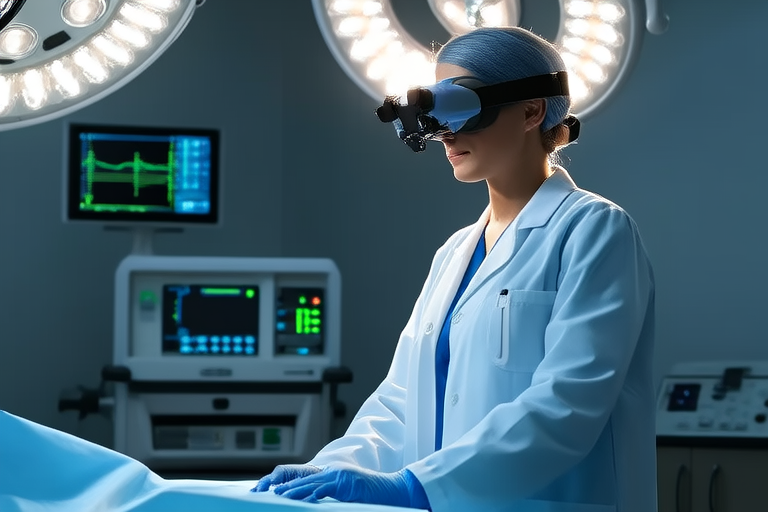
One of the most promising applications of VR and AR in healthcare is in medical training. Surgical simulations using VR allow medical students and professionals to practice procedures in a risk-free environment. These simulations provide an immersive, hands-on experience that enhances learning and prepares practitioners for real-world scenarios.
For instance, companies like Osso VR offer platforms that simulate orthopedic surgeries, helping surgeons refine their techniques without the risks associated with live operations. Similarly, AR can overlay real-time anatomical data onto patients during surgery, providing critical information that aids in precise interventions.
Patient Care and Therapy
VR and AR are also revolutionizing patient care, particularly in pain management and physical therapy. Virtual reality environments can distract patients from pain, making it easier to manage chronic conditions. For example, SnowWorld, a VR game designed to reduce pain perception, has been shown to be effective in treating burn victims.
Additionally, AR can assist in physical therapy by providing real-time feedback on patient movements. Apps like Hocoma’s ArmeoSpring use AR to guide patients through exercises, ensuring they perform them correctly and effectively. In mental health, VR is being used to treat anxiety disorders, phobias, and PTSD through exposure therapy in controlled environments.
Surgical Assistance
The integration of VR and AR in surgeries is improving precision and enhancing outcomes. Surgeons can use AR to visualize internal organs and structures in real-time, which aids in minimally invasive procedures. Companies like AccuVein use AR to project veins onto the skin, making it easier for healthcare providers to locate them accurately.
Case studies have demonstrated the success of these technologies in complex surgeries. For example, AR-assisted spinal surgeries have resulted in reduced operating times and fewer complications. These advancements underscore the potential of VR and AR to transform surgical practices and patient care.
Section 2: VR and AR in Other Industries
Education
VR and AR are enhancing learning experiences in schools and universities by creating immersive educational tools. Students can explore historical events, visit distant planets, or dive into microscopic worlds, all within the safety and convenience of their classrooms. Platforms like Google Expeditions offer virtual field trips to places around the world, while AR apps like Anatomy 4D bring complex biological concepts to life.
These technologies foster deeper engagement and understanding, making learning more interactive and memorable. As educational institutions increasingly adopt VR and AR, the potential for personalized and adaptive learning experiences grows exponentially.
Training and Professional Development
VR and AR are also playing a pivotal role in employee training across various sectors. These technologies provide realistic, hands-on training that prepares workers for real-world challenges. In aviation, pilots can train in simulated cockpits that replicate the experience of flying actual aircraft. Automotive manufacturers use VR to train mechanics on complex vehicle systems, while manufacturers employ AR to guide assembly line workers through intricate tasks.
Industries like construction, logistics, and hospitality are also benefiting from VR and AR training solutions. These technologies ensure that employees are well-prepared for their roles, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Retail and Marketing
VR and AR are revolutionizing customer experiences in retail environments. Virtual try-ons allow customers to see how clothing or accessories look without physically trying them on. Interactive product displays and augmented shopping experiences provide a more engaging and personalized shopping experience.
Brands like IKEA have successfully implemented AR apps that allow customers to visualize furniture in their homes before purchasing. These innovations not only enhance customer satisfaction but also drive sales and brand loyalty.
Section 3: Future Prospects and Challenges
Emerging Applications
The future of VR and AR holds immense promise, with emerging applications in industries yet to fully embrace these technologies. Remote work and telemedicine are likely to benefit greatly from VR and AR, allowing professionals to collaborate and consult remotely in immersive environments. Social interactions could also be transformed, with virtual meetups and events becoming more lifelike and engaging.
Potential breakthroughs in these areas could lead to significant improvements in productivity, accessibility, and quality of life. As these technologies continue to evolve, their applications will expand, offering even more innovative solutions to complex challenges.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their potential, organizations face several challenges when adopting VR and AR. Cost is a major factor, with high-quality hardware and software often being prohibitively expensive. Accessibility is another concern, as not all users may have access to the necessary equipment or internet connectivity.
User comfort is also a consideration, as prolonged use of VR headsets can cause discomfort or motion sickness. Ethical considerations and privacy concerns must be addressed, particularly in sensitive areas like healthcare and personal data management. Ensuring that these technologies are used responsibly and ethically will be crucial for their widespread adoption.
Conclusion
This article has explored the diverse applications of VR and AR beyond gaming, highlighting their transformative impact on healthcare, education, training, and retail. From medical simulations to virtual shopping experiences, these technologies are reshaping how we learn, work, and interact.
The future of VR and AR is bright, with endless possibilities for innovation and improvement. While challenges remain, the potential benefits far outweigh the obstacles. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in shaping our world.
With optimism and careful consideration, VR and AR will continue to unlock new opportunities and drive progress across multiple industries, enhancing both professional and personal experiences.